Mitochondrial Medicine
Mitochondrial function: production of “cell fuel”
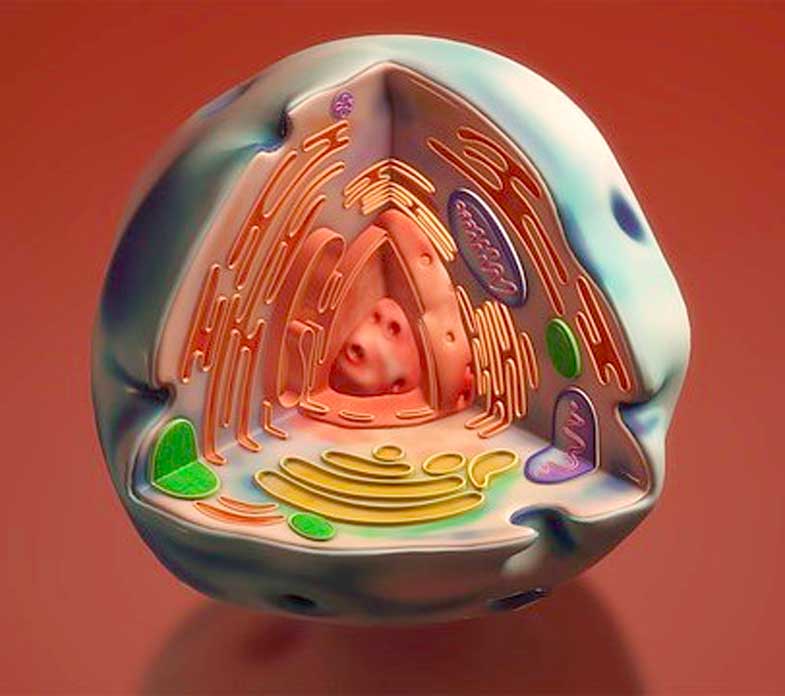

Human cell with various cell organelles (highly simplified illustration). Each body cell has an average of about 1,500 mitochondria (shown here in purple).
Mitochondrial Medicine: Mitochondria are endobionts (internal inhabitants) of the human cell. Mitochondrial medicine takes care of the health of these cell inhabitants.
During evolution, two different types of bacteria, the archaea and the proteo-bacteria, have merged to form a human body cell. Each body cell has about 1,500 mitochondria. Some cells, such as those of the heart muscle, nerves, liver, or egg cells, have up to 50,000 mitochondria.
The entire organism has a total of 180-190 trillion mitochondria. The weight of the human heart is 70% mitochondria. In mitochondria, a huge amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is formed from oxygen, sugar and phosphorus. This is a kind of “cell fuel“. Around the clock, the mitochondria produce as much ATP as the body weighs in kilograms from 90% of the oxygen inhaled.
If a person has 80 kg of body weight, his mitochondria produce 80 kg of ATP for each day.
The cells of the body need ATP as fuel – without a break! The mitochondria are the most diligent shift workers, who only go on strike when they are overloaded with pollutants and/or undernourished. Then, however, there are considerable problems.
But that is not all that these tiny power plants have to do. The energy-providing breakdown of benzoic acid (pyruvate) (produced from glucose) also takes place. The product is called acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle, which also takes place in the mitochondria. This citrate cycle occupies a central position in metabolism – it is also called the “hub of metabolism“.
In addition, fat breakdown takes place in the mitochondria and certain parts of the detoxifying urea cycle are found here. Mitochondria, in addition to bones, are also calcium stores.
Max Plank Society: The endosymbiont theory simply explained
Mitochondriopathy
What is mitochondriopathy?
Mitochondriopathy is a term used to describe mitochondrial dysfunction, sometimes referred to as mitochondrial dysfunction. It can result in a wide range of chronic diseases.
The common feature of mitochondriopathy is: disruption of cell performance and cell control.
What is the effect of the cell malfunction?
There is a slowing down and malfunctioning of the affected cells, comparable to sand in a living gearbox that continuously generates friction losses. The body can compensate for this for a certain time. If a person experiences stress in the form of emotional or physical strain, cell metabolism is massively disturbed. As a result, each person reacts with individual symptoms of illness that reveal their personal weaknesses. And this is where mitochondrial medicine comes into play.
What are the causes of mitochondrial dysfunction?
Confirmed triggers are:
- Toxins from smoking, heavy metals, chemical poisons, pesticides, insecticides, solvents.
- Infections by viruses, bacteria, fungi and other parasites
- Psychological traumas
- Physical traumas, especially in the head and neck area
Amplifying triggers are:
- Mental or physical stress
- Mental or physical overload
- Medications (antibiotics, statins, aspirin, beta blockers, sexual enhancers, nitrates, painkillers, blood pressure medications, etc.)
- Pro-inflammatory diet and inflammatory processes in the body.
NO gas formation and mitochondrial function.
Due to stress load, the cells of the body produce NO gas (nitric oxide). For the discovery of NO gas formation, the Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded in 1998! Until 1970, the physiological NO gas effect in the human organism was unknown. Nitric oxide causes improved blood flow in the body through vasodilatation.
Likewise, NO gas is the first-line defense of the immune system and is produced to defend against intracellular infections, such as viruses, fungi and parasites. In the case of an acute viral infection or chronic inflammation, an acute or a chronic NO gas war takes place in the organism, respectively! The uncontrolled NO gas production leads to interactions in the cell, which in the end irreversibly block the function of the mitochondria.
In addition, nitrosative stress occurs, i.e. the formation of oxygen radicals O-, which react with NO gas and form extremely reactive ONOO-. Its far more aggressive metabolite peroxinitrite triggers a biochemical vicious circle, which Prof. Martin Pall (Washington State University, Institute of Molecular Biology) calls the NO/ONOO cycle. This causes permanent damage to the cell and mitochondrial membranes and genes.
What is the course of mitochondrial dysfunction?
During ATP formation in the mitochondria with the help of oxygen, reactive oxygen free radicals and nitrogen monoxide are normally produced, which are immediately neutralized by antioxidants in functional mitochondria. If this is not the case, these free oxygen radicals can significantly damage the mitochondrial membranes and the cell’s DNA (oxidative stress). Like a magnet, they look for a reaction partner with which they can form a bond, triggering a chain reaction of membrane and cell nucleus damage. If the cells are also permanently stimulated by infections, psychological or physical stress, this creates a chronic NO gas war in the body (see above) with the formation of nitrogen radicals with fatal consequences (nitrosative stress).
During the ATP formation of the mitochondria with the help of oxygen, reactive free oxygen radicals and nitric oxide are normally formed, which are immediately neutralized by antioxidants in functional mitochondria. If this is not the case, these oxygen free radicals can significantly affect the mitochondrial membranes and the DNA of the cell (oxidative stress). Like a magnet, they seek out a reaction partner with which they form a bond, thus triggering a chain reaction of membrane and cell nucleus damage. If continuous stimulation of the cells by infections, psychological or physical stress is added to this, this creates a chronic NO gas war in the body (see above) with the formation of nitrogen radicals with fatal consequences (nitrosative stress).
Diagnostics in the context of mitochondrial medicine: how to detect mitochondriopathy?
With the help of special laboratory diagnostics, mitochondriopathy can be detected reliably and easily.
Mitochondrial dysfunction: There is slowing down and malfunction of the affected cells, comparable to sand in a living gear that continuously generates friction losses.
Mitochondrial medicine in focus: what is mitochondrial therapy?
In mitochondrial medicine, the oxygen-dependent energy production (ATP = cell gasoline) is to be activated and the associated performance of the organs and cells improved. For this, it must be ensured that all building materials for the enzymes are available. In order for the enzymes to work properly, a balanced acid-base status and a discharge of possible toxins in the body (blockage of the enzymes) is required.
In the context of mitochondrial medicine, a combination of different therapies comes into play here:
- Micronutrient substitution, orally or as infusion therapy
- Intestinal rehabilitation and regulation of the intestinal microbiome
- Change of diet
- Heavy metal detoxification
- Elimination of electro-smog and other environmental toxins
- Oxygen therapy by means of IHHT
- Dental rehabilitation if necessary
- If necessary regulatory medicine
Mitochondrial medicine as prevention
Some of the mentioned treatment options are not only recommended for existing complaints, but also preventively: a balanced, organic diet with a large portion of fresh vegetables and fruits, daily exercise in the fresh air if possible, reduction of electrosmog as well as a balanced lifestyle with sufficient sleep are the prerequisites for a healthy organism and are thus an excellent, preventive mitochondrial therapy.
In the THERA Praxisklinik, micronutrient therapy is embedded in the “Cellsymbiosis” therapy concept.
Dysfunction of mitochondria is directly related to the most common diseases of civilization.
IHHT Oxygen Therapy
IHHT (Interval hypoxia-hyperoxie therapy) in particular is an excellent treatment option to regenerate mitochondria.
Mitochondrial therapy
Mitochondrial system therapy involves passing an electric current through the body to improve cell receptivity to infusion therapy. It is an integral part of integrative mitochondrial medicine at THERA Praxisklinik.
Conclusion on mitochondrial medicine
Mitochondria are involved in essential metabolic processes in the body and are present in large numbers in every cell of the body. In the structure and care of your body’s own mitochondria therefore lies an important key to the prevention, healing and relief of your complaints.
Advanced topics (selection):
Your contact persons
Contact and appointment possible at any time
Do one or more of the above points apply to you and would you like to do something for your health? Are you curious? Please feel free to contact us by phone to make an appointment.
You can reach us according to our opening hours at tel. 030 79016533. We look forward to your call or message.